 |
In January 2018, the European Commission adopted the European Strategy for Plastics in a Circular Economy (COM(2018) 28 final), proposing a vision where innovative materials and alternative feedstocks to fossil resources are used for plastic production, wherever these are proven to be more sustainable than traditional non-renewable alternatives. As an implementing measure, the strategy thus includes actions aimed at investigating and better understanding the potential life-cycle impacts of using alternative feedstocks for plastic production (see Annex I to the Strategy). In this context, the Joint Research Centre (JRC) was requested by DG GROW (Directorate-General for Internal Market, Industry, Entrepreneurship and SMEs) to conduct a project focusing on Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) of plastic products derived from different feedstocks, as described in this page. |
Objective
The objective of the project was to:
 |
|
Main steps
The project was developed following a participatory process, involving interested stakeholders at different key steps through public technical consultations and calls for data. The main project steps included:
|
|
|
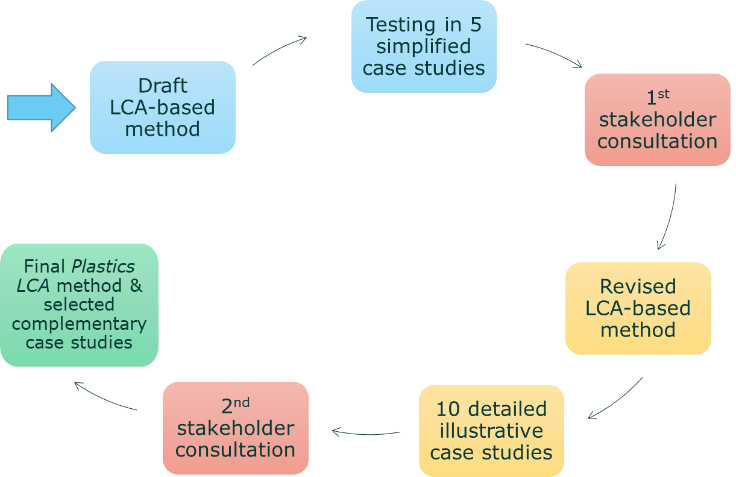 |
Beyond the two public consultations, interested stakeholders were also given the opportunity to provide relevant data and information for the development of the project during two calls for data, in summer 2018 and spring 2019.
Outcomes
The main project outcome is a proposal of common and harmonised methodological framework the - Plastics LCA method - to evaluate and communicate the potential environmental impacts of plastic products derived from different feedstocks. The Plastics LCA method builds upon and fully conforms to the general structure, logic and rules of the EU Product Environmental Footprint (PEF) method. Accordingly, it aims at enabling as much as possible consistent, reproducible, robust, transparent and verifiable LCA studies of plastic products at the EU level.
A number of complementary illustrative case studies are also provided, to facilitate understanding and practical application of the procedural, methodological and modelling rules of the Plastics LCA method by companies and other interested users.
Publications and dissemination

